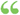 Zir(n — m)t (3); which shews that the intermittent vibration in question is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n + m, n — m. This is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed by Mayer. Zir(n — m)t (3); which shews that the intermittent vibration in question is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n + m, n — m. This is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed by Mayer.  The Theory of Sound - Page 72by John William Strutt Baron Rayleigh - 1894 - 326 pagesFull view The Theory of Sound - Page 72by John William Strutt Baron Rayleigh - 1894 - 326 pagesFull view - About this book
 | Charles Davison - 1889 - 616 pages
...Mag. S. 5. Vol. 27. No. 169. June 1889. 2 I which shows that in this case the intermittent vibration is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n + m, n — m. In order to distinguish wave-frequencies, whose difference is small, a correspond ingly long series... | |
 | John William Strutt Baron Rayleigh - Sound - 1894 - 516 pages
...trigonometrical transformation (2) may be put in the form 2 cos 2irnt + cos 27r (n + m) t + cos 27r (n — m) t (3) ; which shews that the intermittent vibration...is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed byMayer. The form (2) is of course only a particular case. Another in which the intensity of the intermittent... | |
 | Joseph Peterson - Hearing - 1908 - 172 pages
...the intermittent vibration is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n — w, and n -\- m. This is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed by Mayer."110 From tones that are periodically interrupted Koenig went to periodically variable tones.... | |
 | June Etta Downey - Control (Psychology) - 1908 - 500 pages
...the intermittent vibration is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n — m, and n -}- m. This is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed by Mayer."110 From tones that are periodically interrupted Koenig went to periodically variable tones.... | |
 | Psychology - 1908 - 480 pages
...the intermittent vibration is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n — m, and n + m. This is the explanation of the secondary sounds observed by Mayer."110 From tones that are periodically interrupted Koenig went to periodically variable tones.... | |
 | 624 pages
...t + cos 2tr (n — m) t; ............ (7) which shows that in this case the intermittent vibration is equivalent to three simple vibrations of frequencies n, n + m, n — m. * " The pitch of a sonorous body vibrating freely cannot be defined with any greater closeness than... | |
| |