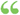 EFC, cutting the circle at F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F, to C. 3. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in the diameter, draw... EFC, cutting the circle at F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F, to C. 3. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in the diameter, draw...  A Course in Mechanical Drawing - Page 26by John Simpson Reid - 1898 - 128 pagesFull view A Course in Mechanical Drawing - Page 26by John Simpson Reid - 1898 - 128 pagesFull view - About this book
 | Peter Nicholson - 1809 - 426 pages
...F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F, to C. 3. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in the diameter, draw CD. 5. Join AD, it will be the side of... | |
 | Edward Shaw - Architecture - 1832 - 402 pages
...F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F to С. 3. Divide the diameter AB, into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in die diameter, draw С D. 5. Join AD ; it will be the side... | |
 | William Templeton (engineer.) - 1833 - 224 pages
...octagon required. PROBLEM XI. In a given Circle, to inscribe any regular Polygon. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides ; from A and B as centres, with the distance AB, describe arcs cutting each other in C ; draw a line... | |
 | Edward Shaw - Architecture - 1836 - 438 pages
...F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F to C. 3. Divide the diameter AB, into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in the diameter, draw С D. 6. Join AD ; it will be the side... | |
 | Peter Nicholson, Joseph Gwilt - Architectural drawing Technique - 1848 - 750 pages
...at F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F to c. 3. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From c, through the second division in the diameter, draw CD. PROBLEM XXIV. PLATE 13. Upon a given... | |
 | Minard Lafever - Architecture - 1849 - 306 pages
...polygon of six equal sides ; from 6, as centre, with fhe given side for radius, describe semi-circle; divide the semi-circle into as many equal parts as the polygon is to have sides, viz. in this case, six, and through the points of division 2, 3, 4, draw the straight... | |
 | Edward Shaw - Architecture - 1852 - 426 pages
...at F. 2. Divide EF into four equal parts, and set three parts from F to C. 3. Divide the diameter AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides. 4. From C, through the second division in the diameter, draw С D. 5. Join AD ; it will be the side... | |
 | Richard Burchett - 1855 - 164 pages
...polygon. FIG. 34. The same — another method. Draw a diameter, AB, of the given circle. Divide AB into as many equal parts as the polygon is required to have sides, by Fig. 13. From A and B, with the line AB as radius, describe arcs, cutting in С. Draw a line from... | |
 | Philip Henry Delamotte - 1874 - 146 pages
...polygon, having the circumscribing circle given. — Draw a tangent AB meeting the circle in C. — From C, with any radius, describe a semicircle cutting...semicircle into as many equal parts as the polygon is to have sides. Draw lines from C through each division. The points where these lines cut the circle... | |
 | James Martin (of the Wedgwood inst, Burslem.) - 1876 - 334 pages
...in this case, say towards the left. With A as centre and AB as radius, describe the semicircle. 2. Divide the semicircle into as many equal parts as the polygon is to have sides (five). 3. From A draw A 2, to the second division of the semicircle. This makes another... | |
| |